Summary of High Voltage Circuit Breaker Control with Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED)
Introduction
Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) have revolutionized the control and automation of high voltage (HV) circuit breakers in substations. By integrating advanced digital technology, IEDs enable real-time monitoring, management, and control from a centralized remote hub, enhancing the efficiency, reliability, and safety of power systems.
Installation and Integration
A circuit breaker control IED can be installed either within the circuit breaker cabinet in the switchyard or in the relay/control room. It is important to note that functions such as Breaker Failure (BF), Auto Reclose (AR), and Circuit Supervision (CS) are typically not integrated into the Breaker Control IED but may be handled by separate protective relays or other devices.
Signal Consolidation
In some substation applications, instead of having individual trip/close wires for each protective or control IED connected to the same circuit breaker, a single circuit breaker control IED can consolidate all trip or close signals from multiple IEDs. This approach simplifies wiring and reduces the number of connections, making the system more efficient and easier to maintain.
Monitoring and Auxiliary Functions
The circuit breaker control IED continuously monitors the status of the circuit breaker, including:
Position Status: Open, closed, or intermediate positions.
Pressure Levels: Hydraulic, pneumatic, or gas pressure, which are critical for proper operation.
Auxiliary Contacts: Used to provide status information to related IEDs
Additionally, the IED provides several auxiliary functions:
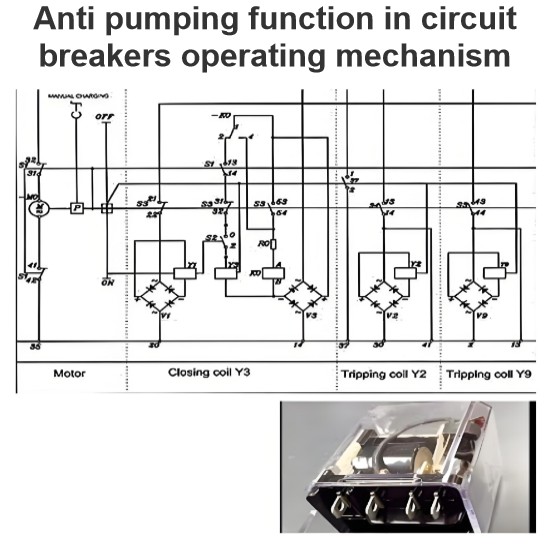
Anti-pumping Function: Prevents the circuit breaker from being reclosed until the cause of the failure has been addressed. If an anti-pump function exists in the circuit breaker itself, the IED's anti-pump function should be disabled to avoid conflicts.
Circuit Breaker Coil Supervision: Monitors the health of the trip and close coils to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Pressure Supervision: Alerts operators to low pressure conditions and blocks tripping/closing commands if the pressure is insufficient.
Main Functions of a Circuit Breaker Control IED
Acquisition of Primary Switch Status Information: The IED collects data on the position and status of the circuit breaker.
Execution of Trip/Close Commands: The IED can execute trip or close commands locally or remotely via SCADA, Bay Control Units, or protection IEDs.
Phase-Segregated Tripping and Closing: The IED can independently trip or close individual phases (A, B, C) or perform three-phase operations. However, it does not include integrated logic for pole discrepancy.
Anti-Pumping Function: Prevents the circuit breaker from being repeatedly closed during a fault condition.
Circuit Breaker Coil Supervision: Ensures the integrity of the trip and close coils.
Pressure Supervision: Monitors pressure levels to ensure safe operation and prevents unsafe actions.
Signal Interaction in Circuit Breaker IED
When a power system fault occurs:
Protection IEDs detect the fault and issue a trip command to the Breaker Control IED.The Breaker Control IED then trips the corresponding circuit breaker using hardwired signals (Phase A, B, C, or 3-phase tripping).After tripping, the IED acquires the new status of the circuit breaker (e.g., open or closed) and provides this information to relevant IEDs via hardwired signals.Additional status information, such as low pressure, is also monitored and reported.The trip signal from protection IEDs is also used to initiate the Auto Reclose (AR) function, which attempts to restore power after a fault. The AR close command is sent to the Breaker Control IED via hardwired signals. Similarly, the trip signal can initiate the Breaker Failure (BF) function, and re-trip signals are also hardwired to the IED.Remote control commands (opening/closing) from RTU/SCADA, local substation automation systems, or Bay Control Units are also hardwired to the circuit breaker control IED.
Communication with IEC 61850 and GOOSE
In modern substations, the Breaker Control IED can communicate using the IEC 61850 protocol, specifically through GOOSE (Generic Object-Oriented Substation Event) messages. This allows for seamless integration with other intelligent devices in the substation, reducing the need for hardwired connections and improving system flexibility and reliability.
Figure 1 illustrates a typical application of a circuit breaker control IED using GOOSE communication. In practice, redundant networks (Network A and Network B) are often implemented to ensure higher reliability.
Role in Substation Automation
The Breaker Control IED acts as a digital interface between secondary devices (such as protection IEDs, SCADA systems, and Bay Control Units) and the high-voltage primary equipment (circuit breakers). It facilitates the transition from traditional analog systems to fully digitalized substations, enabling advanced features like real-time monitoring, automated control, and improved fault handling.

Other Main functions of circuit breaker control IED:
In figure 2 show circuit breaker control IED functional and signal interactions:

Comprehensive Overview of High Voltage Circuit Breaker Control with Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED)
Introduction
Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) play a crucial role in modern substations by enabling advanced control and monitoring of high voltage (HV) circuit breakers. The Circuit Breaker Controller is a specialized IED that gathers information from circuit breakers and sends control commands to them, facilitating real-time management and automation. This device interfaces with traditional analog signal-based breakers through hardwired input/output contacts, converting electrical signals into digital data for communication via the IEC 61850 protocol and GOOSE (Generic Object-Oriented Substation Event) messages.
Key Functions of the Circuit Breaker Controller
Gathering Information from Breakers
Position Status: Open, closed, or intermediate positions.
Control Pressure Status: Hydraulic, pneumatic, or gas pressure levels.
Auxiliary Contacts: Additional status signals such as low pressure, fault conditions, etc.
Hardwired Inputs: The Circuit Breaker Controller uses hardwired input contacts to gather various status information from the circuit breakers, including:
Analog-to-Digital Conversion: The controller converts these analog signals into digital format, making the data compatible with modern communication protocols.
Sending Control Commands to Breakers
Hardwired Outputs: The Circuit Breaker Controller uses hardwired output contacts to send trip or close commands to the circuit breakers. These commands are executed based on instructions received from protective devices, SCADA systems, or bay control units.
Phase-Segregated Circuits: The controller typically provides phase-segregated tripping and closing circuits, allowing independent control of individual phases (A, B, C) or three-phase operations. For a three-phase circuit breaker, it usually provides one close coil and two trip coils.
Communication via GOOSE Messages
Publishing Information to Bay Level Devices: After gathering electrical information from the circuit breakers, the Circuit Breaker Controller converts this data into digital signals and publishes it to bay level IEDs via the process bus using GOOSE messages. This allows other devices in the substation to access real-time status updates.
Receiving GOOSE Messages from Bay Level Devices: When a power system fault occurs or a remote control command is issued, the related protective devices or bay control units publish corresponding GOOSE messages (e.g., trip command, close command). The Circuit Breaker Controller, acting as a subscriber, receives these messages and takes appropriate actions, such as tripping or closing the circuit breaker via its hardwired output contacts.
Repeated Tripping Prevention (Anti-Pump Function)
Preventing Repeated Tripping: If a circuit breaker is manually or automatically closed on a permanent fault and the closing signal persists, the breaker may attempt to close multiple times after each trip. To prevent this, the Circuit Breaker Controller includes an anti-pump function that ensures the breaker trips only once and prevents further closing until the closing circuit is de-energized by the operator.
Configuration Consideration: If the circuit breaker itself has an anti-pump circuit, the anti-pump function in the Circuit Breaker Controller should be disabled to avoid conflicts.
Circuit Breaker Coil Supervision
Close Coil Supervision: The Circuit Breaker Controller can monitor the status of the close coil using auxiliary relays. This is achieved by connecting the terminal to the negative pole of the power supply in series with the normally closed auxiliary contact (52b) of the circuit breaker. If the terminal is also connected to the close coil (CC), the auxiliary relays can provide supervision of the close coil's health.
Trip Coil Supervision: Similarly, the controller can supervise the status of the trip coil using auxiliary relays. This is done by connecting the terminal to the negative pole of the power supply in series with the normally open auxiliary contact (52a) of the circuit breaker. If the terminal is also connected to the trip coil (TC), the auxiliary relays can monitor the trip coil's condition.
Pressure Supervision and Blocking
Critical Pressure Monitoring: The pressure in circuit breakers is essential for their proper operation. Abnormal pressure levels can lead to malfunctions, reduced lifespan, or even damage to the breakers. Therefore, the Circuit Breaker Controller monitors all types of pressure signals (e.g., hydraulic, pneumatic, gas) in the related circuit breakers.
Pressure Block Functions: When a trip or close command is received, the controller implements pressure block functions to prevent unsafe operations. If the pressure is below a safe threshold, the controller will block the execution of the command to protect the breaker. These block functions ensure that the circuit breaker operates only under safe conditions.
Phase-Segregated Tripping and Closing Circuits
The Circuit Breaker Controller typically provides phase-segregated tripping and closing circuits, allowing independent control of each phase. For a three-phase circuit breaker, the controller usually includes:
One Close Coil: Used to close all three phases simultaneously.
Two Trip Coils: One for single-phase tripping and another for three-phase tripping. This design allows for flexible and precise control of the circuit breaker, depending on the specific requirements of the power system.
Conclusion
The Circuit Breaker Controller is a vital component in modern substations, bridging the gap between traditional analog circuit breakers and digital communication systems. By integrating advanced features such as GOOSE message communication, anti-pump functionality, and coil supervision, the controller enhances the reliability, safety, and efficiency of high-voltage circuit breaker operations. Its ability to gather real-time data and execute control commands ensures that substations can operate smoothly, even in complex and dynamic power environments.