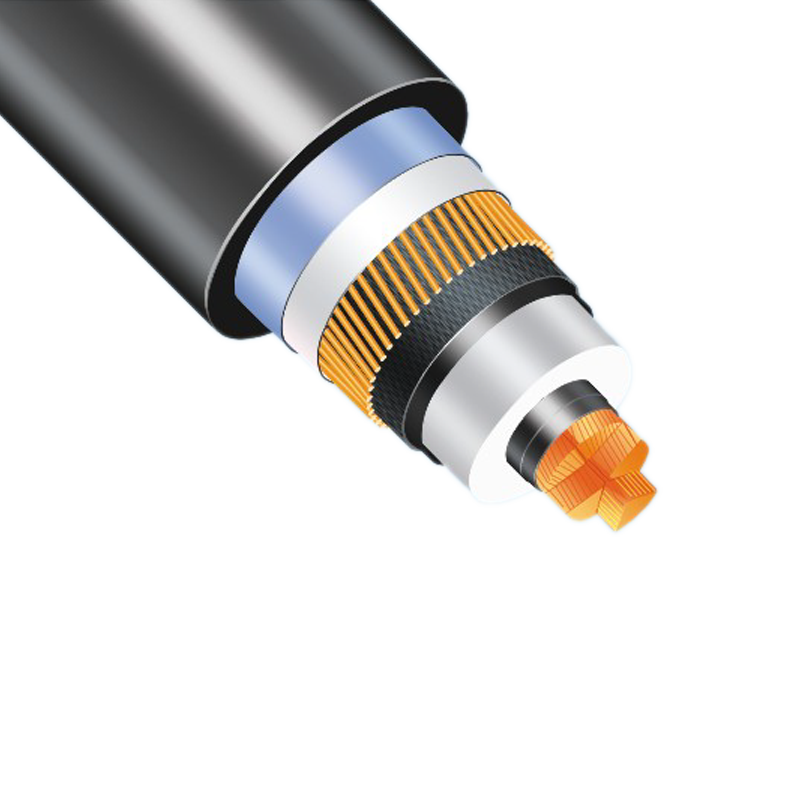
| Brand | Wone Store |
| Model NO. | YJA Series cross-linked cable |
| Rated voltage | 500KV |
| number of core | 1-core |
| Nominal cross-sectional area | 2500F |
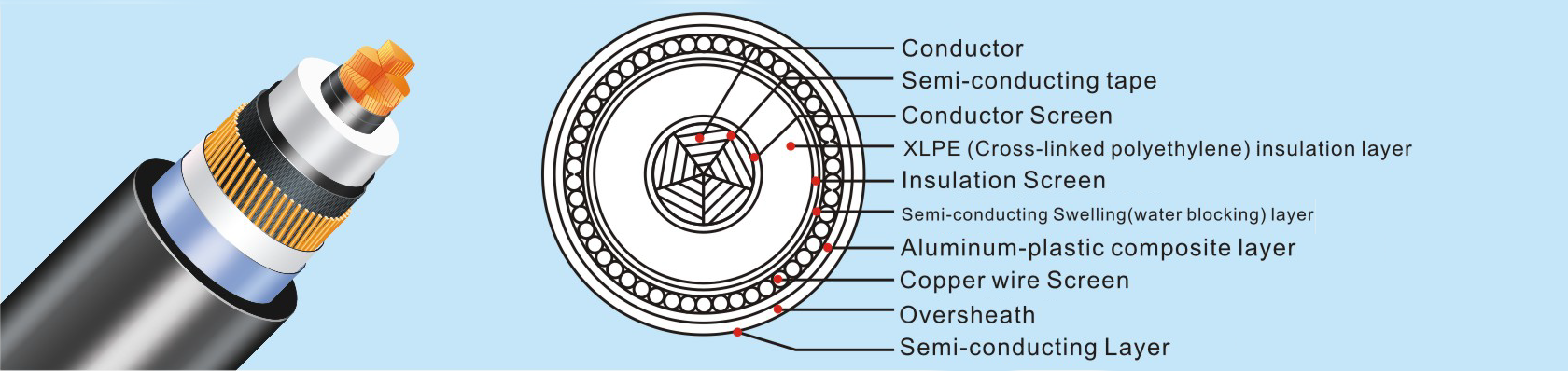
| cable insulation structure | XLP insulation&Eplastic-Al composite layer&PVC sheath |
| Conductor type | Cu-core |
| Series | YJA Series |
Overview
This productis suitable for 110-500kV power transmission and distribution system for thetransmission of electrical energy, low smoke no accounting for the flameretardant performance higher than the national standard, widely used inairports, nuclear power plants, key water control projects, high-risebuildings, Chemical, metallurgy, petroleum, traffic and other flame-retardantproperties demanding places.
Implementationstandards
66-132kV product implementationstandards: GB / T 11017 and GB / T 19666, the flame retardant properties inline with GB / T 18380 requirements;
220-500kV product implementationstandards: GB / T 18890 and GB / T 19666, the flame retardant properties inline with GB / T 18380 requirements.
Name and structure
Model |
Name | |
Cu-core |
Al-core |
|
YJA02 |
YJLA02 |
Cross - linked polyethylene insulated, aluminum - plastic composite sheath and polyvinyl chloride sheathed power cable. |
YJA03 |
YJLA03 |
Cross - linked polyethylene insulated, aluminum - plastic composite sheath and polyethylene sheathed power cable. |
parameters
66KV cross-linked power cable
Nominal cross-sectional area mm² |
Diameter of conductor mm |
Nominal thickness of insulation mm |
Thickness of aluminum sheath mm |
Thickness of over sheath mm |
Approximation outer diameter mm |
Approximate Weight(kg/km) |
|||
Copper (Cu)- PVC sheath |
Copper (Cu)- PE sheath |
Aluminum (Al)- PVC sheath |
Aluminum (Al)- PE sheath |
||||||
240 |
18.5 |
13.5 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
66 |
6452 |
6135 |
4982 |
4665 |
300 |
20.7 |
13.5 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
69 |
7156 |
6830 |
5314 |
4988 |
400 |
23.5 |
13.5 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
71 |
8108 |
7770 |
5752 |
5414 |
500 |
26.5 |
13.5 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
74 |
9299 |
8947 |
6273 |
5921 |
630 |
29.8 |
13.5 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
79 |
10824 |
10459 |
6912 |
6547 |
800 |
33.8 |
13.0 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
83 |
12585 |
12207 |
7575 |
7197 |
800F |
35.0 |
13.0 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
86 |
13226 |
12792 |
8216 |
7782 |
1000F |
39.2 |
13.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
91 |
15403 |
14949 |
9116 |
8662 |
1200F |
42.0 |
13.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
95 |
17159 |
16691 |
9831 |
9363 |
1400F |
46.0 |
13.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
98 |
19245 |
18761 |
10664 |
10180 |
1600F |
48.6 |
13.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
101 |
21240 |
20742 |
11444 |
10946 |
110KV cross-linked power cable
Nominal cross-sectional area mm² |
Diameter of conductor |
Nominal thickness of insulation |
Thickness of aluminum sheath mm |
Thickness of over sheath mm |
Approximation outer diameter mm |
Approximate Weight(kg/km) |
|||
Copper (Cu)- PVC sheath |
Copper (Cu)- PE sheath |
Aluminum (Al)- PVC sheath |
Aluminum (Al)- PE sheath |
||||||
240 |
18.5 |
19.0 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
76 |
7665 |
7297 |
6195 |
5827 |
300 |
20.7 |
18.5 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
77 |
8285 |
7912 |
6443 |
6070 |
400 |
23.5 |
17.5 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
78 |
9035 |
8658 |
6679 |
6302 |
500 |
26.5 |
17.0 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
80 |
10139 |
9753 |
7113 |
6727 |
630 |
29.8 |
16.5 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
83 |
11804 |
11367 |
7892 |
7455 |
800 |
33.8 |
16.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
86 |
13596 |
13145 |
8586 |
8135 |
800F |
35.0 |
16.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
90 |
14056 |
13587 |
9046 |
8577 |
1000F |
39.2 |
16.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
94 |
16268 |
15779 |
9981 |
9492 |
1200F |
42.0 |
16.0 |
0.25 |
5.0 |
98 |
18300 |
17753 |
10972 |
10425 |
1400F |
46.0 |
16.0 |
0.25 |
5.0 |
102 |
20448 |
19879 |
11867 |
11298 |
1600F |
48.6 |
16.0 |
0.25 |
5.0 |
105 |
22478 |
21893 |
12862 |
12097 |
132KV cross-linked power cable
Nominal cross-sectional area mm² |
Diameter of conductor mm |
Nominal thickness of insulation |
Thickness of aluminum sheath mm |
Thickness of over sheath mm |
Approximation outer diameter |
Approximate Weight(kg/km) |
|||
Copper (Cu)- PVC sheath |
Copper (Cu)- PE sheath |
Aluminum (Al)- PVC sheath |
Aluminum (Al)- PE sheath |
||||||
240 |
18.5 |
19.5 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
77 |
7782 |
7410 |
6312 |
5940 |
300 |
20.7 |
19.0 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
79 |
8404 |
8026 |
6562 |
6184 |
400 |
23.5 |
19.0 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
81 |
9401 |
9011 |
7045 |
6655 |
500 |
26.5 |
19.0 |
0.25 |
4.0 |
84 |
10639 |
10237 |
7613 |
7211 |
630 |
29.8 |
19.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
89 |
12461 |
12001 |
8549 |
8089 |
800 |
33.8 |
18.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
91 |
14136 |
13667 |
9126 |
8657 |
800F |
35.0 |
18.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
94 |
14617 |
14129 |
9607 |
9119 |
1000F |
39.2 |
18.0 |
0.25 |
4.5 |
99 |
16854 |
16347 |
10567 |
10060 |
1200F |
42.0 |
18.0 |
0.25 |
5.0 |
103 |
18912 |
18346 |
11584 |
11018 |
1400F |
46.0 |
18.0 |
0.25 |
5.0 |
106 |
21079 |
20490 |
12498 |
11909 |
1600F |
48.6 |
18.0 |
0.25 |
5.0 |
109 |
23127 |
22522 |
13331 |
12726 |
220KV cross-linked power cable
Nominal cross-sectional area mm² |
Diameter of conductor |
Nominal thickness of insulation |
Thickness of aluminum sheath mm |
Thickness of over sheath mm |
Approximation outer diameter |
Approximate Weight(kg/km) |
|
Copper (Cu)- PVC sheath |
Copper (Cu)- PE sheath |
||||||
400 |
23.5 |
27.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
100 |
12690 |
12027 |
500 |
26.5 |
27.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
103 |
14018 |
13338 |
630 |
29.8 |
26.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
104 |
15371 |
14684 |
800 |
33.8 |
25.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
106 |
17116 |
16411 |
800F |
35.0 |
25.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
110 |
17666 |
16941 |
1000F |
39.2 |
24.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
112 |
19669 |
18929 |
1200F |
42.0 |
24.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
115 |
21537 |
20779 |
1400F |
46.0 |
24.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
119 |
23750 |
22971 |
1600F |
48.6 |
24.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
122 |
25883 |
25080 |
1800F |
52.0 |
24.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
125 |
27902 |
27079 |
2000F |
55.2 |
24.0 |
0.30 |
5.0 |
128 |
30188 |
29348 |
500KV cross-linked power cable
Nominal cross-sectional area mm² |
Diameter of conductor mm |
Nominal thickness of insulation mm |
Thickness of aluminum sheath mm |
Thickness of over sheath mm |
Approximation outer diameter |
Approximate Weight(kg/km) |
|
Copper(Cu)- PVC sheath |
Copper (Cu)- PE sheath |
||||||
800 |
33.8 |
34.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
131 |
20215 |
19510 |
800F |
35.0 |
34.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
133 |
20547 |
19822 |
1000F |
39.2 |
33.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
135 |
22602 |
21862 |
1200F |
42.0 |
33.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
138 |
24527 |
23769 |
1400F |
46.0 |
32.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
140 |
26822 |
26043 |
1600F |
48.6 |
32.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
143 |
29031 |
28228 |
1800F |
52.0 |
31.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
144 |
31119 |
30296 |
2000F |
55.2 |
31.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
147 |
33480 |
32640 |
2200F |
57.4 |
31.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
150 |
35283 |
34429 |
2500F |
61.5 |
31.0 |
0.35 |
6.0 |
154 |
38445 |
37568 |
Usefeatures
1、Maximum rated temperature
Long-term maximum allowable operatingconductor temperature: 90 ℃,Maximum operating temperature under short-timeoverload: 105 90 ℃,Maximum operating temperature under short circuit (shortcircuit duration 5 s): 250 ℃
2、Installation requirements
Cable laying shall not be restrictedby drop height; the ambient temperature for laying shall not be lower than 0 90 ℃;C,and if the ambient temperature is lower than 0 90 ℃, the cable shall bepre-heated.
2.1Minimum bending radius of cable
During cablelaying: 20D0; and Permanentinstallation: 15D0.
Note: D0 is measured outerdiameter of cable.
2.2Maximum allowable axial traction for cable installation, T (radial sidepressure at bend not being considered)
Conductor: T=K x Conductor section (kg)
Aluminum sheath:T x Aluminum sheath section(kg)
Where, the coefficient K=7kg/mm2for copper conductor and 4kg/mm2 for aluminum conductor and 2kg/mm2 for aluminum sheath.
2.3Maximumallowable side pressure when cable is bent, P
P=T/R≤500(kg/m), where T is axialtraction, and R is bending radius.